KNOW MORE ABOUT HEADACHE
A headache is a secondary symptom, characterized by pain in the head caused by various conditions. It occurs due to the stimulation (mechanical, chemical, etc.) of sensory structures inside or outside the skull.
Headaches are a highly prevalent symptom in clinical epidemiological studies. In Europe and the United States, headaches are among the most common complaints encountered by healthcare professionals.

Sensitive Pain Structures in the Skull-Facial Region:
-
Skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscles, extracranial arteries, and the cranial bones.
-
Structures sensitive to pain in the ears, eyes, nasal cavity, and sinuses.
-
Intracranial venous sinuses, especially around the sinuses.
-
The meninges of the brain and arteries.
-
Middle meningeal artery, superficial temporal artery.
-
Cranial nerves V, VII, IX, X; the first three cervical nerve roots (C1, C2, C3).
Causes of Headaches
Neurological Causes:
-
Traumatic brain injury.
-
Meningitis, cerebrovascular disease.
-
Increased intracranial pressure syndrome.
-
Migraine.
-
Functional disorders.
Headaches due to systemic diseases:
-
Acute systemic infections.
-
Toxicity.
-
Heatstroke, sunstroke.
Internal Medicine-related Causes:
-
Cardiovascular diseases.
-
Digestive diseases.
-
Chronic kidney disease.
-
Anemia.
-
Endocrine disorders.
Other Specialized Causes (Eyes, Ears, Nose, Throat):
-
Skull bone inflammation, Paget's disease of bone.
-
Cancer metastasis to the skull bones.
-
Cervical spine deformities.
-
Greater occipital nerve pain due to cervical spondylosis.
-
Herniated cervical discs.
-
Temporal arteritis (Horton’s disease).
Headache Symptoms
Headaches are classified into three main types:
-
Tension Headache
-
Migraine
-
Cluster Headache
Each type presents different symptoms, such as dull, sharp, throbbing, or stabbing pain; sometimes lasting only a few minutes, or extending for days.
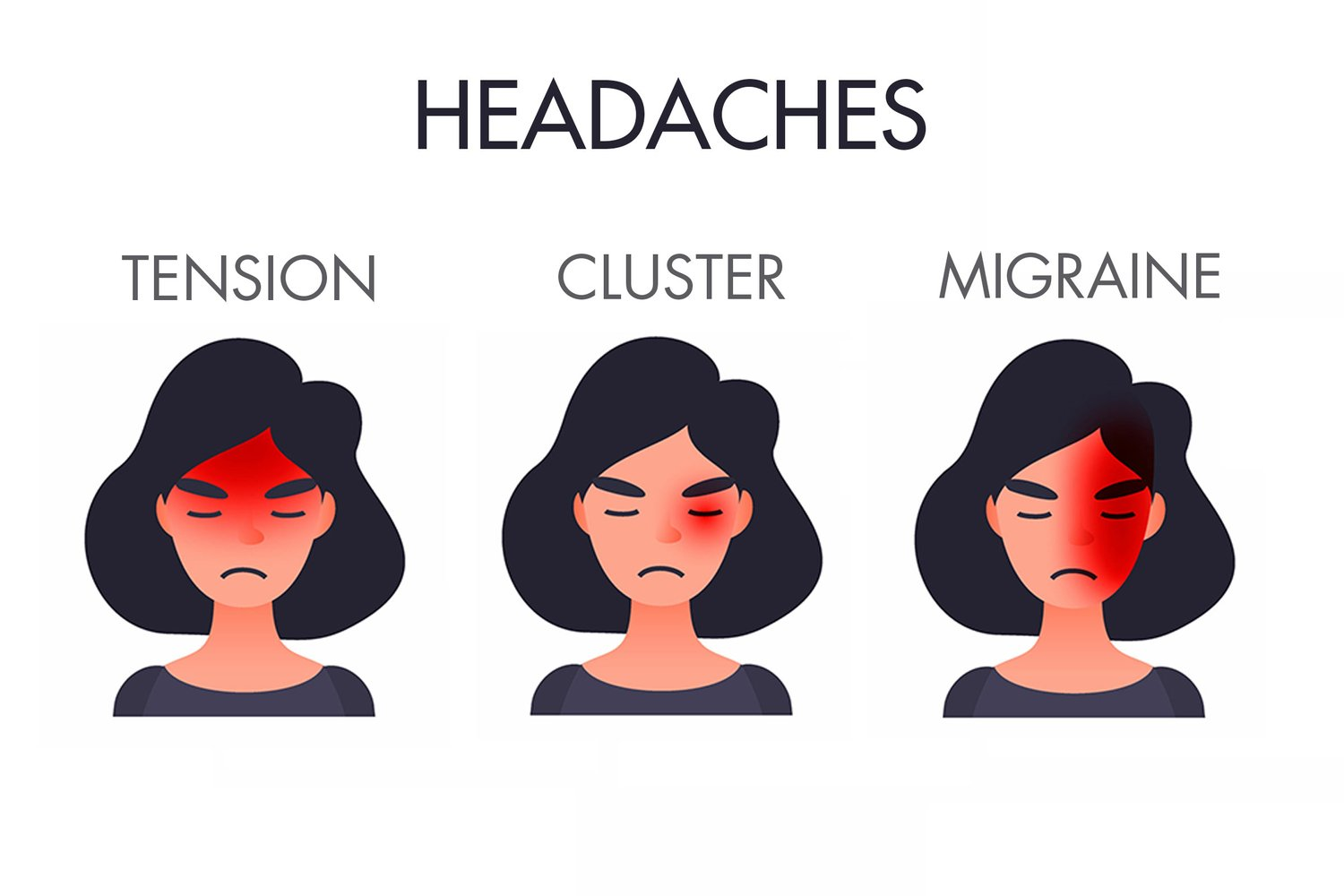
Symptoms of Tension Headache
-
Pain intensity varies from mild to moderate, with a sensation of tightness, like a band around the head.
-
Usually affects both sides of the head and is short-lived, causing discomfort and frustration.
Symptoms of Migraine
-
Intense, throbbing pain on one side of the head.
-
Migraine sufferers are sensitive to light and noise.
-
Nausea and vomiting may occur with this type of headache.
-
The pain can last from several hours to days and may recur.
Symptoms of Cluster Headache
-
Sharp, localized pain often around one eye.
-
Starts on one side of the head, around and behind the eye, becoming more severe, lasting from 15 minutes to 3 hours.
-
May be accompanied by eye swelling, tearing, redness, and nasal congestion or a runny nose on the affected side.
Before treatment, it is crucial to identify the type of headache in order to provide effective care and prevention.
Risk Groups for Headache
Headaches can affect anyone, from men to women, and from children to the elderly. However, certain groups are more commonly affected:
-
Women: Migraines in particular are often triggered by hormonal fluctuations, such as during menstruation or menopause.
-
Individuals with low systolic blood pressure or a large difference between their blood pressure readings may be at higher risk.
-
Those who consume alcohol, caffeine, or are under stress, sleep-deprived, or dealing with anxiety are more prone to headaches.
-
Office workers, particularly those who spend long hours on computers without breaks.
Headache Prevention
-
Limit exposure to noisy environments or bright lights (such as watching movies in a theater or staring at the sun) as these can trigger migraines.
-
Reduce mental stress and relax before and after long working hours.
-
Office workers should change positions frequently and take 30-second breaks every hour. Pay attention to relaxing the jaw, neck, shoulders, and upper back muscles.
-
Regular physical exercise (20-30 minutes daily) can help reduce stress. Activities like walking or yoga are ideal.
-
Get adequate sleep—7-8 hours each night can help prevent fatigue, headaches, and stress, improving productivity.
-
Limit alcohol, caffeine, and other stimulants, as excessive consumption can exacerbate headaches. Gradually reduce caffeine intake to avoid withdrawal headaches.
-
Avoid self-medication, as some drugs may cause headaches as a side effect.
-
Stay hydrated, aiming for 2-2.5 liters of water daily, especially in hot weather, as dehydration can lead to dizziness, fatigue, and headaches.
-
Consume foods rich in vitamin E, such as black sesame seeds, which help balance estrogen levels and reduce headaches, especially in women during menstruation.
In case you would like to relieve from the pain quickly, we have fast on-set product: Paracetamol in solution/suspension or Dexibuprofen-softcap
